Hani Dbouk, M. Sc.
Erstbetreuer: S. Schön; Co-Betreuer: I. Neumann
This dissertation project deals with the development of alternative integrity measures based on interval analysis and set theory. For selected sensors from the central experimental facility, remaining random and systematic errors have been described using error bands in the form of intervals.
We have derived error bands in three different ways: from a predefined integrity risk, by sensitivity analysis of the influence parameters for correction models, and from expert knowledge of the selected sensors and the experimental area.
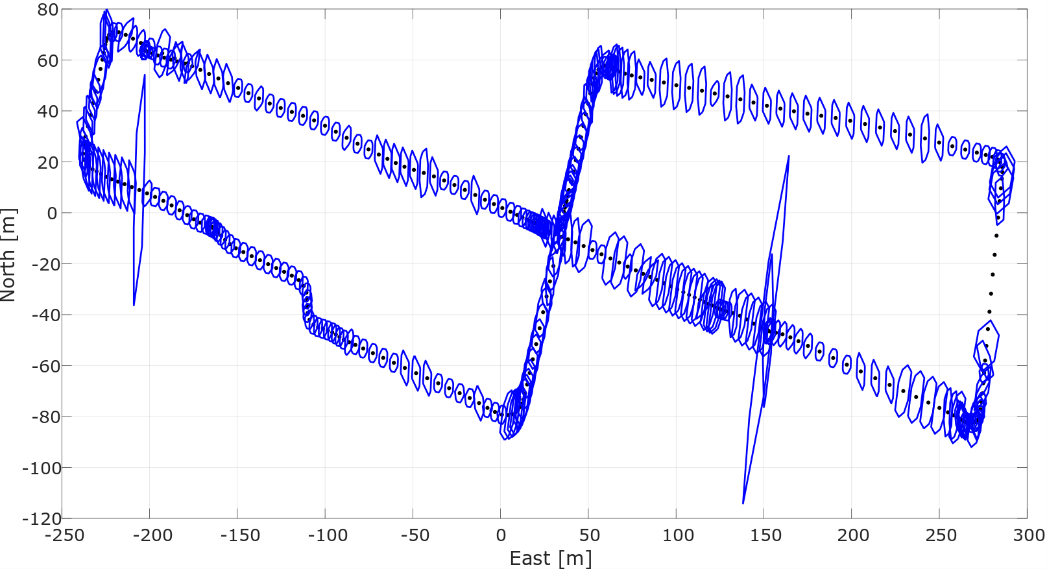
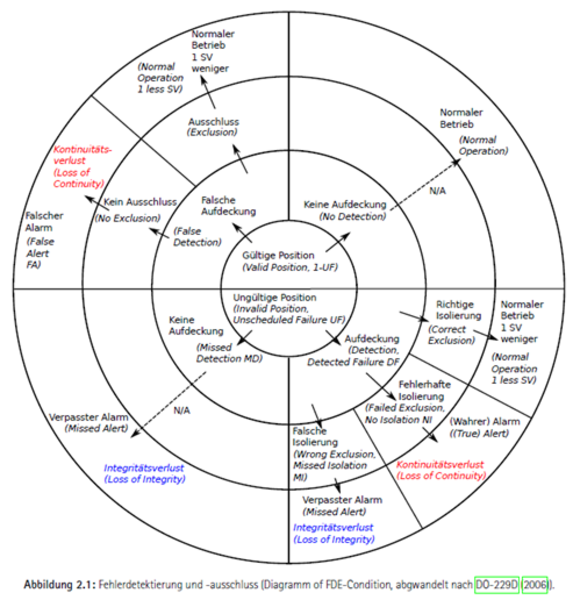
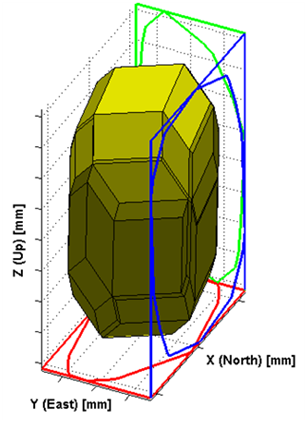
Then, the error bands are transferred to the navigation problem by means of geometrical constraints. The navigation problem becomes a convex optimization problem that provides a polytope feasible region for all possible solution and zonotope as a confidence domain. Afterwards, a fault detection and excluding algorithm was developed based on the polytope and zonotope-bounding zone that provides a guaranteed protection level. In addition to that, guaranteed upper bound on the minimum detectable bias is derived from the zonotopal bounding zone and an actual minimum detectable bias is derived from the fault detection and excluding algorithm.
Further, the newly developed integrity approach is compared to the two most used, classical stochastic integrity approaches in a simulated and real data, where our interval-based approaches outperform both purely stochastic methods in terms of accuracy, reliability, and integrity.
Schneiderberg 50
30167 Hannover
Schneiderberg 50
30167 Hannover